What is DevOps?
DevOps is a software development practice that promotes collaboration between development and operations, resulting in faster and more reliable software delivery. Commonly referred to as a culture, DevOps connects people, process, and technology to deliver continuous value.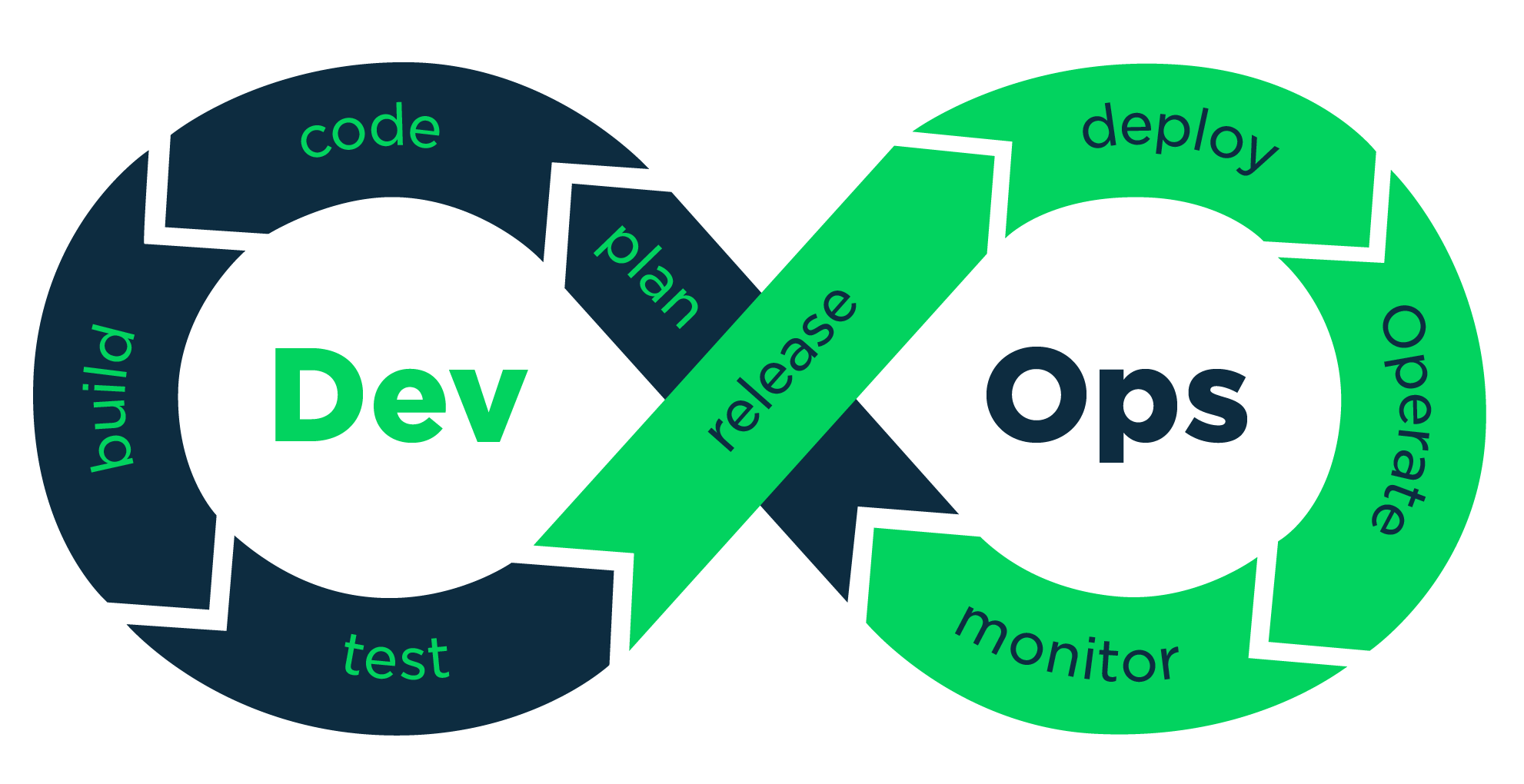
DevOps definition
A compound of development (Dev) and operations (Ops), DevOps is the union of people, process and technology to continually provide value to customers.
- What does DevOps mean for teams? DevOps enables formerly siloed roles—development, IT operations, quality engineering and security—to coordinate and collaborate to produce better, more reliable products. By adopting a DevOps culture along with DevOps practices and tools, teams gain the ability to better respond to customer needs, increase confidence in the applications they build and achieve business goals faster.
Overview
DevOps combines development and operations to increase the efficiency, speed, and security of software development and delivery compared to traditional processes. A more nimble software development lifecycle results in a competitive advantage for businesses and their customers.
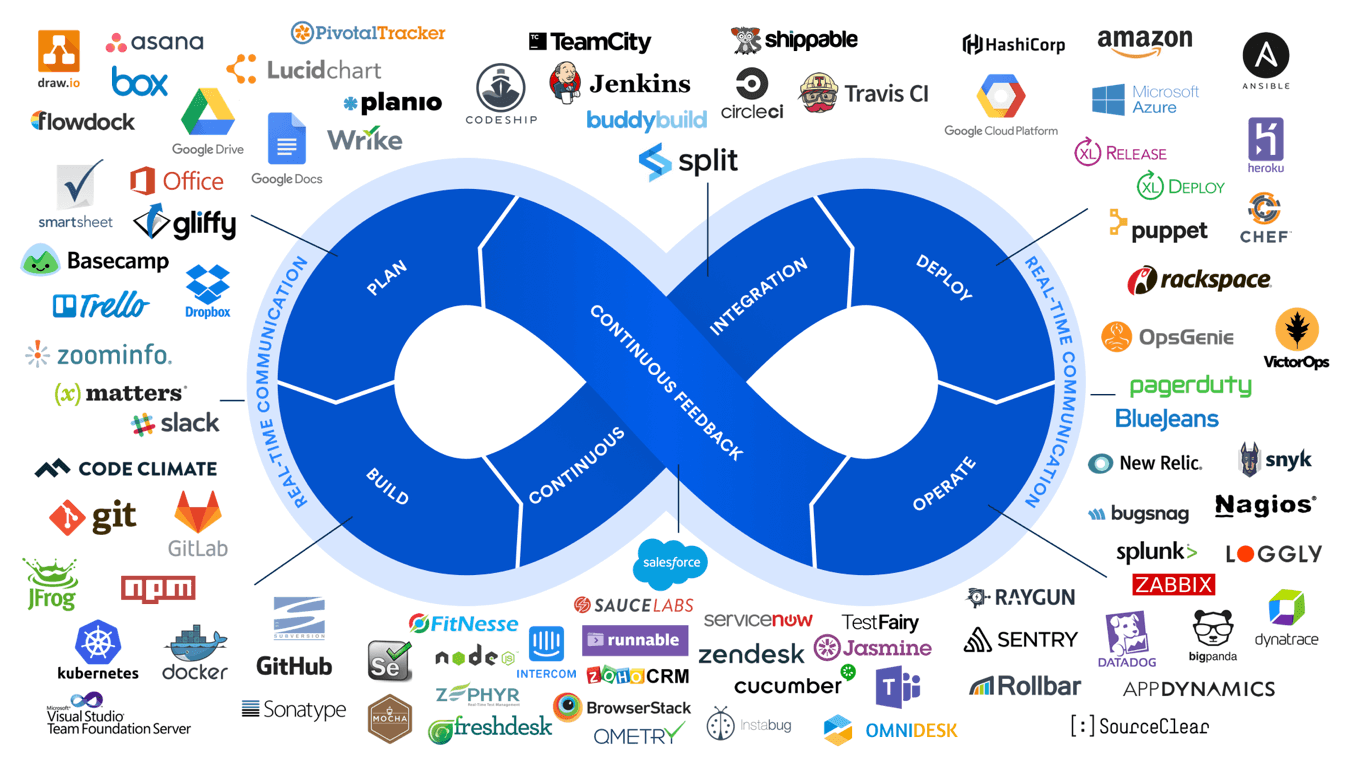
The benefits of DevOps
Teams that adopt DevOps culture, practices and tools become high-performing, building better products faster for greater customer satisfaction. This improved collaboration and productivity is also integral to achieving business goals like these:
 Accelerating time to market
Accelerating time to market
 Adapting to the market and competition
Adapting to the market and competition
 Maintaining system stability and reliability
Maintaining system stability and reliability
 Improving the mean time to recovery
Improving the mean time to recovery
DevOps and the application lifecycle
DevOps influences the application lifecycle throughout its plan, develop, deliver and operate phases. Each phase relies on the others and the phases are not role-specific. In a true DevOps culture, each role is involved in each phase to some extent.
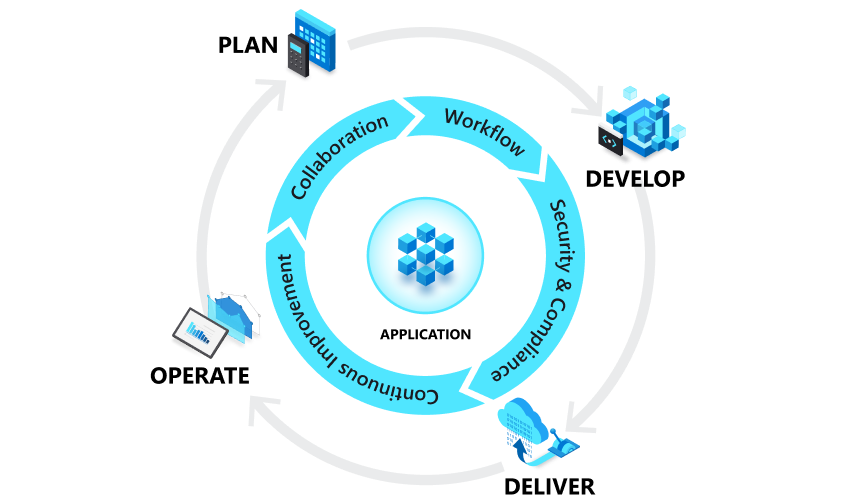
Plan
In the plan phase, DevOps teams ideate, define, and describe features and capabilities of the applications and systems they are building. They track progress at low and high levels of granularity—from single-product tasks to tasks that span portfolios of multiple products.
Develop
The develop phase includes all aspects of coding—writing, testing, reviewing and the integration of code by team members—as well as building that code into build artifacts that can be deployed into various environments. DevOps teams seek to innovate rapidly without sacrificing quality, stability and productivity.
Deliver
Delivery is the process of deploying applications into production environments in a consistent and reliable way. The deliver phase also includes deploying and configuring the fully governed foundational infrastructure that makes up those environments
Operate
The operate phase involves maintaining, monitoring and troubleshooting applications in production environments. In adopting DevOps practices, teams work to ensure system reliability, high availability and aim for zero downtime while reinforcing security and governance. DevOps teams seek to identify issues before they affect the customer experience and mitigate issues quickly when they do occur.
DevOps culture
While adopting DevOps practices automates and optimises processes through technology, it all starts with the culture inside the organisation—and the people who play a part in it. The challenge of cultivating a DevOps culture requires deep changes in the way people work and collaborate. But when organisations commit to a DevOps culture, they can create the environment for high-performing teams to develop.
 Collaboration, visibility and alignment
Collaboration, visibility and alignment
One hallmark of a healthy DevOps culture is collaboration between teams, which starts with visibility.
 Shifts in scope and accountability
Shifts in scope and accountability
As teams align, they take ownership and become involved in additional lifecycle phases—not just the ones central to their roles. For example, developers become accountable not only to the innovation and quality established in the develop phase
 Shorter release cycles
Shorter release cycles
DevOps teams remain agile by releasing software in short cycles. Shorter release cycles make planning and risk management easier since progress is incremental, which also reduces the impact on system stability.
 Continuous learning
Continuous learning
High-performing DevOps teams establish a growth mindset. They fail fast and incorporate learnings into their processes, continually improving, increasing customer satisfaction and accelerating innovation and market adaptability.